os 模块就是对操作系统进行操作
shell命令就是linux系统的命令(类似于window下命令行里的命令)
文件路径问题: 如果文件路径是当前项目下的,那么在路径开头是不用加 /,否则无法读取文件
1. 目录相关操作
- os.getcwd() -> 获取当前的工作目录,即当前 Python 脚本工作的目录路径
import os
os.getcwd() # D:\Learning Python\Python 基础
- os.chdir('路径') -> 改变当前工作目录到指定的路径,相当于window命令行和linux shell 的 cd
import os
os.chdir(r'D:\Learning Python')
- os.curdir -> 返回当前目录 .
import os
print(os.curdir) # .
- os.pardir -> 返回当前目录的父目录字符串名 ..
import os
print(os.pardir) # ..
2. 文件夹的相关操作
- os.makedirs('foldername1/foldername2') -> 创建多层的嵌套文件夹
import os
os.makedirs('文件夹1/文件夹2/文件夹3')
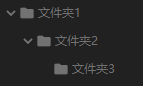
- os.removedirs('foldername1') -> 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推
import os
os.removedirs('文件夹1/文件夹2/文件夹3')
- os.mkdir('foldername') -> 创建单个文件夹
import os
os.mkdir('文件夹')
- os.rmdir('foldername') -> 删除单个空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错
import os
os.rmdir('文件夹')
- os.listdir('foldername') -> 列出指定路径下的一级目录下的文件和文件夹,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印
import os
list_dir = os.listdir('D:\Learning Python\Python 基础')
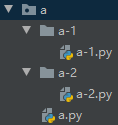
import os
list_dir = os.listdir('a')
print(list_dir) # ['a-1', 'a-2', 'a.py']
- os.walk('foldername') -> 获取指定路径下的所有文件和文件夹,返回值: 对象,可以对该对象进行循环
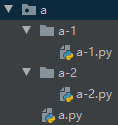
import os
# ------------------------------------------
obj_walk = os.walk('a')
print(obj_walk) # <generator object walk at 0x0000021848B3B830>
# ------------------------------------------
for obj in os.walk('a'):
print(obj)
"""
打印结果:
# 第一个值: 当前路径
# 第二个值: 当前路径下的所有文件夹
# 第三个值: 当前路径下的所有文件
('a', ['a-1', 'a-2'], ['a.py'])
('a\\a-1', [], ['a-1.py'])
('a\\a-2', [], ['a-2.py'])
"""
# ------------------------------------------
for base_path, folder_list, file_list in os.walk('a'):
"""
base_path: 当前路径
folder_list: 当前路径下的所有文件夹
file_list: 当前路径下的所有文件
"""
print(base_path, folder_list, file_list)
"""
打印结果:
a ['a-1', 'a-2'] ['a.py']
a\a-1 [] ['a-1.py']
a\a-2 [] ['a-2.py']
"""
- 获取指定目录下的所有py文件
import os
target_path = 'a'
for base_path, folder_list, file_list in os.walk(target_path):
for file_name in file_list:
file_path = os.path.join(base_path, file_name) # 获取文件路径
file_ext = file_path.rsplit('.', maxsplit=1) # 获取后缀名
if len(file_ext) != 2 or file_ext[1] != 'py': # 如果没有后缀名或后缀名不是py的那么就跳出当前循环
continue
with open(file_path, mode='rb') as f:
print(f)
"""
打印结果:
<_io.BufferedReader name='a\\a.py'>
<_io.BufferedReader name='a\\a-1\\a-1.py'>
<_io.BufferedReader name='a\\a-2\\a-2.py'>
"""
3. 文件的相关操作
- os.remove('filename') -> 删除一个文件
import os
os.remove('filename.txt')
- os.rename("oldname","newname") -> 重命名文件/目录
import os
os.rename('filename1.txt', 'filename2.txt')
- os.stat('path/filename') -> 获取文件/目录信息
import os
stat = os.stat('file.txt')
print(stat) # os.stat_result(st_mode=33206, st_ino=79938893386144019, st_dev=748152, st_nlink=1, st_uid=0, st_gid=0, st_size=221, st_atime=1548378599, st_mtime=1548378599, st_ctime=1548378489)
st_mode | inode 保护模式 |
st_ino | inode 节点号 |
st_dev | inode 驻留的设备 |
st_nlink | inode 的链接数 |
st_uid | 所有者的用户ID |
st_gid | 所有者的组ID |
st_size | 普通文件以字节为单位的大小;包含等待某些特殊文件的数据 |
st_atime | 上次访问的时间 |
st_mtime | 最后一次修改的时间 |
st_ctime | 由操作系统报告的"ctime"。在某些系统上(如Unix)是最新的元数据更改的时间,在其它系统上(如Windows)是创建时间(详细信息参见平台的文档) |
4. 运行shell命令
- os.system('shell命令') -> 运行shell命令,直接显示,没有返回值
import os
os.system('dir')
- os.popen('shell命令').read() -> 运行shell命令,有返回值
import os
pop = os.popen('dir').read()
print(pop)
5. 路径相关的操作
- os.path.abspath('路径') -> 返回 path 规范化的绝对路径
import os
os_path = os.path.abspath(__file__)
# 等同于
os_path = os.path.abspath('file.txt')
print(os_path) # D:\Learning Python\Python 基础\file.txt
- os.path.split('路径') -> 将路径分割成目录和文件名二元组返回
import os
os_path = os.path.split(r'D:\Learning Python\Python 基础\file.txt')
print(os_path) # ('D:\\Learning Python\\Python 基础', 'file.txt')
- os.path.dirname('路径') -> 返回路径的目录,其实就是 os.path.split(path) 的第一个元素
import os
os_path = os.path.dirname(r'D:\Learning Python\Python 基础\file.txt')
print(os_path) # D:\Learning Python\Python 基础
- os.path.basename('路径') -> 返回路径最后的文件名,如何路径以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值,即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素
import os
os_path = os.path.basename(r'D:\Learning Python\Python 基础\file.txt')
print(os_path) # file.txt
- os.path.exists('路径') -> 判断路径是否存在,返回True/False
import os
os_path = os.path.exists(r'D:\Learning Python\Python 基础\file.txt')
print(os_path) # True
- os.path.isabs('路径') -> 判断路径是否是绝对路径,返回 True/False
import os
os_path = os.path.isabs(r'D:\Learning Python\Python 基础\file.txt')
print(os_path) # True
- os.path.isfile('路径') -> 判断文件是否存在,返回True/False
import os
os_path = os.path.isfile(r'D:\Learning Python\Python 基础\file.txt')
print(os_path) # True
- os.path.isdir('路径') -> 判断目录是否存在,返回True/False
import os
os_path = os.path.isdir(r'D:\Learning Python\Python 基础')
print(os_path) # True
- os.path.join(path1, path2, path3) -> 将多个路径组合后返回一个新路径
import os
next_path = os.path.join(r'D:\Learning Python', 'Python 基础', 'file.txt')
print(next_path) # D:\Learning Python\Python 基础\file.txt
- os.path.getatime('路径') -> 返回路径所指向的文件或者目录的最后访问时间的时间戳
import os
access_time = os.path.getatime(r'D:\Learning Python\Python 基础\file.txt')
print(access_time) # 1548378599.2095585
- os.path.getmtime('路径') -> 返回路径所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间的时间戳
import os
edit_time = os.path.getmtime(r'D:\Learning Python\Python 基础\file.txt')
print(edit_time) # 1548378599.2095585
- os.path.getsize('路径') -> 返回文件夹/文件的大小(返回文件夹的大小是不准的,如果要获取文件夹的大小就将里面的文件的大小全部加起来)
import os
file_size = os.path.getsize(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'file.txt'))
print(file_size) # 221
- os.path.splitext('路径') -> 将路径和文件后缀名切割成列表 -> 一般用于获取文件后缀名
import os
suffix_list = os.path.splitext('a/b/test.txt')
print(suffix_list) # ('a/b/test', '.txt')
print(suffix_list[1]) # .txt
5. 跨平台所使用的相关操作
- os.sep -> 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为'\',Linux下为'/'
import os
path_separator = os.sep
print(path_separator) # \ win下为'\',Linux下为'/'
- os.linesep -> 输出当前平台使用的换行符,win下为'\r\n',Linux下为'\n'
import os
terminator = os.linesep
print(terminator)
- os.pathsep -> 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串 win下为';',Linux下为':'
import os
pathsep = os.pathsep
print(pathsep) # ;
- os.name -> 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win -> 'nt'; Linux -> 'posix'
import os
os_name = os.name
print(os_name) # nt
6. 其他
- os.urandom(num) -> 随机生成长度为num位的bytes类型
import os
msg = os.urandom(5) # 随机生成长度为5位的bytes类型
print(msg) # b'\xda\x7f\xbcz~'
print(len(msg)) # 5
- os.getpid() -> 获取当前进程的 pid
import os
print(os.getpid()) # 248 获取当前进程的 pid
- os.getpid() -> 获取当前父进程的 pid
import os
print(os.getppid()) # 5604 获取当前父进程的 pid